Retention of hydrogen isotopes in materials bombarded with high energy ion beams
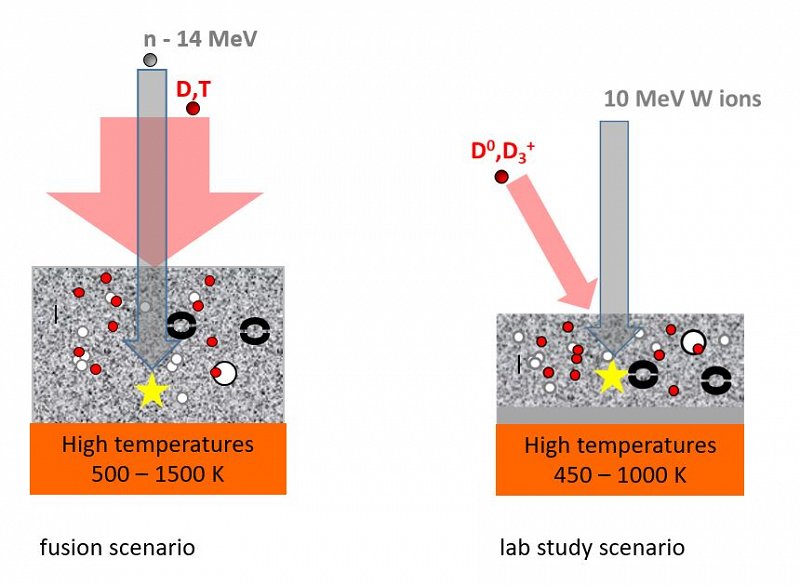
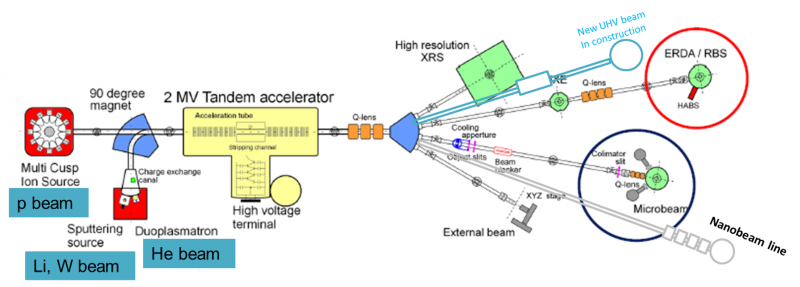
The PhD thesis would first include experimental work on a new ultra high vacuum beam line intended for homogeneous irradiation of materials to create defects in the crystal lattice and then study hydrogen interaction with such a material. As part of the doctoral work, the candidate would finish setting up the new beam line and make it operational. The next step would be to study the evolution of defects in the crystal lattice of the material (fusion steel) caused by high-energy particle bombardment at different exposure conditions such as different irradiation dose, effect of temperature, presence of hydrogen during defect creation or influence of helium. Finally, deuterium retention and transport in such material will be studied with advanced ion beam methods. The PhD work would also include modelling of physical processes that will help to understand the experimental results.
The studies would take place at two experimental stations located at the 2 MV tandem accelerator, within the laboratory for fusion research, in a dynamic and relaxed environment.
Related references:
- Markelj S. et al., Phys. Scr. 97 (2022) 024006
- Markelj S. et al. Nucl. Fusion 59 (2019) 086050
Contact: Doc. Dr Sabina Markelj